Rated Acupoints
Acupuncture Treatment For Heartburn
BACK TO THE TOP
Heartburn is a condition that is characterized by burning sensation in our chest or abdomen. The pain may radiate to the neck, throat, or angle of the jaw.
1
CONTENTS
SYMPTOMS
CAUSES
TREATMENTS
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of Heartburn are difficulty swallowing, chronic cough, stomach pain, constant sore throat, regurgitation of foods, and persistent hoarseness.
2
CAUSES
Heartburn is a part of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). It is mainly caused by backflow of stomach acid to the esophagus. This backflow can caused by many things including alcohol, caffeine, aspirin, and carbonated beverages. Other things that can cause heartburn including smoking, hiatal hernia, pregnancy, obesity, and other disease of the esophagus.
3
TREATMENTS
Related Acupuncture Points :
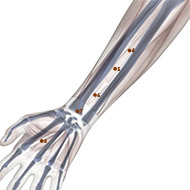
P6
Acupuncture Treatment For Heartburn
The heartburn is happen because there is acid backflow from the stomach to the chest of human body. This condition is one of many symptoms of GERD. The acupuncture treatment for this condition will be performed at various acupoints including Zhongwan (CV 12), bilateral Zusanli (ST36), Sanyinjiao (SP6), and Neiguan (PC6). The treatment will be perform everyday for the first week. Then, the treatment will be continue for subsequent week with interval of 2-3 days between treatment. After receiving treatment, it is hoped that the intraesophageal acid and bile reflux can be stopped.
4
BACK TO THE TOP
Footnotes
- Heartburn, From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heartburn
- Heartburn (Acid Reflux), Medical Author: Jerry R. Balentine, DO, FACEP, http://www.medicinenet.com/heartburn_reflux/article.htm
- Heartburn,rxlist.com, http://www.rxlist.com/heartburn/drugs-condition.htm#heartburn_causes
- Clinical study on the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux by acupuncture., ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20697939
LU01
LU02
LU03
LU04
LU05
LU06
LU07
LU08
LU09
LU10
LU11
LI01
LI02
LI03
LI04
LI05
LI06
LI07
LI08
LI09
LI10
LI11
LI12
LI13
LI14
LI15
LI16
LI17
LI18
LI19
LI20
ST01
ST02
ST03
ST04
ST05
ST06
ST07
ST08
ST09
ST10
ST11
ST12
ST13
ST14
ST15
ST16
ST17
ST18
ST19
ST20
ST21
ST22
ST23
ST24
ST25
ST26
ST27
ST28
ST29
ST30
ST31
ST32
ST33
ST34
ST35
ST36
ST37
ST38
ST39
ST40
ST41
ST42
ST43
ST44
ST45
SP01
SP02
SP03
SP04
SP05
SP06
SP07
SP08
SP09
SP10
SP11
SP12
SP13
SP14
SP15
SP16
SP17
SP18
SP19
SP20
SP21
HT01
HT02
HT03
HT04
HT05
HT06
HT07
HT08
HT09
SI01
SI02
SI03
SI04
SI05
SI06
SI07
SI08
SI09
SI10
SI11
SI12
SI13
SI14
SI15
SI16
SI17
SI18
SI19
BL01
BL02
BL03
BL04
BL05
BL06
BL07
BL08
BL09
BL10
BL11
BL12
BL13
BL14
BL15
BL16
BL17
BL18
BL19
BL20
BL21
BL22
BL23
BL24
BL25
BL26
BL27
BL28
BL29
BL30
BL31
BL32
BL33
BL34
BL35
BL36
BL37
BL38
BL39
BL40
BL41
BL42
BL43
BL44
BL45
BL46
BL47
BL48
BL49
BL50
BL51
BL52
BL53
BL54
BL55
BL56
BL57
BL58
BL59
BL60
BL61
BL62
BL63
BL64
BL65
BL66
BL67
KD01
KD02
KD03
KD04
KD05
KD06
KD07
KD08
KD09
KD10
KD11
KD12
KD13
KD14
KD15
KD16
KD17
KD18
KD19
KD20
KD21
KD22
KD23
KD24
KD25
KD26
KD27
PC01
PC02
PC03
PC04
PC05
PC06
PC07
PC08
PC09
TB01
TB02
TB03
TB04
TB05
TB06
TB07
TB08
TB09
TB10
TB11
TB12
TB13
TB14
TB15
TB16
TB17
TB18
TB19
TB20
TB21
TB22
TB23
GB01
GB02
GB03
GB04
GB05
GB06
GB07
GB08
GB09
GB10
GB11
GB12
GB13
GB14
GB15
GB16
GB17
GB18
GB19
GB20
GB21
GB22
GB23
GB24
GB25
GB26
GB27
GB28
GB29
GB30
GB31
GB32
GB33
GB34
GB35
GB36
GB37
GB38
GB39
GB40
GB41
GB42
GB43
GB44
LV01
LV02
LV03
LV04
LV05
LV06
LV07
LV08
LV09
LV10
LV11
LV12
LV13
LV14
GV01
GV02
GV03
GV04
GV05
GV06
GV07
GV08
GV09
GV10
GV11
GV12
GV13
GV14
GV15
GV16
GV17
GV18
GV19
GV20
GV21
GV22
GV23
GV24
GV25
GV26
GV27
GV28
CV01
CV02
CV03
CV04
CV05
CV06
CV07
CV08
CV09
CV10
CV11
CV12
CV13
CV14
CV15
CV16
CV17
CV18
CV19
CV20
CV21
CV22
CV23
CV24