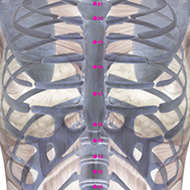
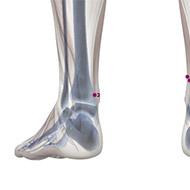
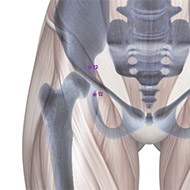
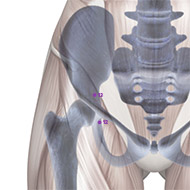
Rated Acupoints
Acupuncture treatment for Alzheimer\'s Disease
Rated Acupoints
2
Rated Acupoints
4
Rated Acupoints
5
Rated Acupoints
6
Rated Acupoints
7
Rated Acupoints
8
Rated Acupoints
9
Rated Acupoints
10
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is one of the most prevalent forms of dementia worldwide. The neuropathological changes of AD are characterized by amyloid-β plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and neuronal loss.1 Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is the most important at-risk state of AD. It has a high probability of degenerating into AD at a rate of 10–15% per year.2 People aged over 60 usually suffer from Alzheimer’s disease, which is characterized by a lack of thinking and language skills, and also behavioral changes. The condition known as Alzheimer’s disease is usually progressive.3 Not only progressive, this condition is also irreversible. Most people begin to suffer this disease at their mid-60s.4 However, there is no effective therapy for AD and MCI. Acupuncture, a treatment of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), remains promising as a therapy to treat neurological diseases including chronic pain, drug addiction, stroke as well as dementia.5
CONTENTS
SYMPTOMS
CAUSES
TREATMENTS
SYMPTOMS
The most common early symptom of Alzheimer’s disease is the difficulty in remembering recent events (short-term memory loss).6 As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioral issues.7 As a person’s condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.8
CAUSES
The cause of Alzheimer’s disease is poorly understood.9 About 70% of the risk is believed to be genetic with many genes usually involved. Other risk factors include a history of head injuries, depression, or hypertension. The disease process is associated with plaques and tangles in the brain.10 In this vein, most of the scientists believe that Alzheimer’s disease is caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle and environmental factors that affect the brain over time. Its effect on the brain is clear. Alzheimer’s disease damages and destroys brain cells. A brain affected by Alzheimer’s disease has many fewer cells and many fewer connections among surviving cells than does a healthy brain.11 As more brain cells die, Alzheimer’s leads to significant brain shrinkage.12 When doctors examine Alzheimer’s brain tissue under the microscope, they see two types of abnormalities that are considered hallmarks of the disease: plaques13 and tangles.14 Therefore, Alzheimer’s disease is caused by damage to the human brain. This damage affects the structure and function of particular brain areas. Some degree of vascular damage in the brain has also been found.15 Other possible causes of this condition could be extreme loneliness, insomnia or anti-anxiety medication,head or brain injury, diabetes and lack of sleep.16
TREATMENTS
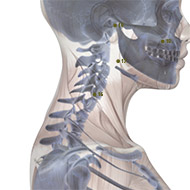
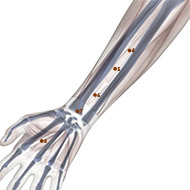
There are four known acupoints for AD: Tai Chong (LIV-3) and He gu (LI-4) in left and right side. These points have shown to activate brain regions consistent with impaired brain function.17 Moreover, it has been found that for the brain resting state after acupuncture, there are several brain regions showing increased or decreased activities in MCI and AD subjects comparing to normal subjects.18 Most of the brain regions were involved in the temporal lobe and the frontal lobe of the brain, which was closely related to memory and cognition. Furthermore, another study revealed that stimulating at Tai Chong (LIV-3) and He gu (LI-4) enhances the hippocampal connectivity in the brain of AD patients.19
In addition to the acupoints mentioned above, the following four acupoints of Shenmen (HT-7), Zusanli (ST-36), Fenglong (ST-40) and Taixi (KD-3) have been demonstrated to activate the right brain main hemisphere (temporal lobe, such as hippocampal gyrus, insula, and some area of parietal lobe) and left activated regions (temporal lobe, parietal lobule, some regions of cerebellum).20 The activated regions induced by these acupoints were consistent with impaired areas in the brain of AD patients, which were closely correlated with brain cognitive function (memory, reason, language, executive, etc).21
Two additional studies have shown that acupuncture alleviates AD by improving verbal and motor skills and altering mood and cognitive function.22 In the first study, subjects were treated twice a week for three months. The initial 10 main acupoints selected were GB-9, GV-16, GV-20, GV-23, GV-24, PC-6, HT-7, SP-6, Sishencong, and Yintang.23 The secondary points selected were ST-36, LI-4, GB-20, GV-17, SP-4, KD-3, SI-3, BL-62, BL-23, GV-26, and the cervical and thoracic Huato Jiaji points.24 Ten acupuncture points emerged as the most frequently used points: GV-20 (in 68% of treatments), Taixi/KI-3 (60%), Zusanli/ST-36 (58%), Sishencong EX-1 (48%), Yintang EX-2 (48%), Sanyinjiao/SP-6 (47%), Shenmen/HT-7 (40%), laser stimulation of the occipital (base of the skull) (40%), GB-9 (35%), and GV-23 (19%).25 As the points were either on the head or on the four limbs, they required minimal or no undressing of the participants. In addition to the acupuncture, the subjects continued using any medications already prescribed.
In the second study, subjects were treated on eight acupoints: the Si Shen Cong (EX-1), four points on the scalp, Shen men (HT-7 on the wrists) and Tai xi (KD-3 on the feet).26 Needling for each acupoint lasted a total of 30 minutes, comprising the needle testing and its reinsertion after every 10 minutes of therapy. Subjects received a seven-day treatment cycle with a three-day break in between for a total of 30 days.27
Another acupoint related to AD is LI-17.
Footnotes
- Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer – Acta Neuropathol – 1991, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1759558
- Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment – Arch Neurol – 2001, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11735772
- About Alzheimer’s Disease – AFA – 2016, http://www.alzfdn.org/AboutAlzheimers/definition.html
- About Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Basics – NIH – 2016, https://www.nia.nih.gov/alzheimers/topics/alzheimers-basics
- Clinical effects of acupuncture combined with nimodipine for treatment of vascular dementia in 30 cases – JTCM – 2009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19894378
- Alzheimer’s disease – BMJ – 2009, http://www.bmj.com/content/338/bmj.b158
- Dementia Fact sheet N°362 – WHO – 2009, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/
- Alzheimer’s disease – NEJM – 2010, http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra0909142
- Alzheimer’s disease – BMJ – 2009, http://www.bmj.com/content/338/bmj.b158
- Alzheimer’s disease – NEJM – 2010, http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra0909142
- Dementia Fact sheet N°362 – WHO – 2009, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/
- Dementia Fact sheet N°362 – WHO – 2009, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/
- Alzheimer’s disease – BMJ – 2009, http://www.bmj.com/content/338/bmj.b158
- Dementia Fact sheet N°362 – WHO – 2009, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs362/en/
- Causes of Alzheimer’s disease – nhs.uk – 2016, http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Alzheimers-disease/Pages/Causes.aspx
- 5 Surprising Causes Of Alzheimer’s Disease – prevention.com – 2015, http://www.prevention.com/health/causes-alzheimers
- Effect of Acupuncture in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: A Functional MRI Study – PlosOne – 2012, http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0042730
- Effect of Acupuncture in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: A Functional MRI Study – PlosOne – 2012, http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0042730
- Acupuncture Modulates Resting State Hippocampal Functional Connectivity in Alzheimer Disease – PlosOne – 2014, http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0091160
- Effect of Acupuncture Given at the HT-7, ST-36, ST-40 and KD-3 Acupoints on Various Parts of the Brains of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients – AETR – 2008, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18672741
- Effect of Acupuncture Given at the HT-7, ST-36, ST-40 and KD-3 Acupoints on Various Parts of the Brains of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients – AETR – 2008, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18672741
- Treating Alzheimer’s Symptoms with Acupuncture – alzheimer.net – 2014, http://www.alzheimers.net/11-19-14-acupuncture-for-alzheimers
- Alzheimer’s disease – yingyanghouse.com – 2017, https://community.yinyanghouse.com/t/alzheimers-disease/2624
- Alzheimer’s disease – yingyanghouse.com – 2017, https://community.yinyanghouse.com/t/alzheimers-disease/2624
- Treating Alzheimer’s Symptoms with Acupuncture – alzheimer.net – 2014, http://www.alzheimers.net/11-19-14-acupuncture-for-alzheimers
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Acupuncture – acupuncturetoday.com – 2000, http://www.acupuncturetoday.com/mpacms/at/article.php?id=27681
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Acupuncture – acupuncturetoday.com – 2000, http://www.acupuncturetoday.com/mpacms/at/article.php?id=27681
LU01
LU02
LU03
LU04
LU05
LU06
LU07
LU08
LU09
LU10
LU11
LI01
LI02
LI03
LI04
LI05
LI06
LI07
LI08
LI09
LI10
LI11
LI12
LI13
LI14
LI15
LI16
LI17
LI18
LI19
LI20
ST01
ST02
ST03
ST04
ST05
ST06
ST07
ST08
ST09
ST10
ST11
ST12
ST13
ST14
ST15
ST16
ST17
ST18
ST19
ST20
ST21
ST22
ST23
ST24
ST25
ST26
ST27
ST28
ST29
ST30
ST31
ST32
ST33
ST34
ST35
ST36
ST37
ST38
ST39
ST40
ST41
ST42
ST43
ST44
ST45
SP01
SP02
SP03
SP04
SP05
SP06
SP07
SP08
SP09
SP10
SP11
SP12
SP13
SP14
SP15
SP16
SP17
SP18
SP19
SP20
SP21
HT01
HT02
HT03
HT04
HT05
HT06
HT07
HT08
HT09
SI01
SI02
SI03
SI04
SI05
SI06
SI07
SI08
SI09
SI10
SI11
SI12
SI13
SI14
SI15
SI16
SI17
SI18
SI19
BL01
BL02
BL03
BL04
BL05
BL06
BL07
BL08
BL09
BL10
BL11
BL12
BL13
BL14
BL15
BL16
BL17
BL18
BL19
BL20
BL21
BL22
BL23
BL24
BL25
BL26
BL27
BL28
BL29
BL30
BL31
BL32
BL33
BL34
BL35
BL36
BL37
BL38
BL39
BL40
BL41
BL42
BL43
BL44
BL45
BL46
BL47
BL48
BL49
BL50
BL51
BL52
BL53
BL54
BL55
BL56
BL57
BL58
BL59
BL60
BL61
BL62
BL63
BL64
BL65
BL66
BL67
KD01
KD02
KD03
KD04
KD05
KD06
KD07
KD08
KD09
KD10
KD11
KD12
KD13
KD14
KD15
KD16
KD17
KD18
KD19
KD20
KD21
KD22
KD23
KD24
KD25
KD26
KD27
PC01
PC02
PC03
PC04
PC05
PC06
PC07
PC08
PC09
TB01
TB02
TB03
TB04
TB05
TB06
TB07
TB08
TB09
TB10
TB11
TB12
TB13
TB14
TB15
TB16
TB17
TB18
TB19
TB20
TB21
TB22
TB23
GB01
GB02
GB03
GB04
GB05
GB06
GB07
GB08
GB09
GB10
GB11
GB12
GB13
GB14
GB15
GB16
GB17
GB18
GB19
GB20
GB21
GB22
GB23
GB24
GB25
GB26
GB27
GB28
GB29
GB30
GB31
GB32
GB33
GB34
GB35
GB36
GB37
GB38
GB39
GB40
GB41
GB42
GB43
GB44
LV01
LV02
LV03
LV04
LV05
LV06
LV07
LV08
LV09
LV10
LV11
LV12
LV13
LV14
GV01
GV02
GV03
GV04
GV05
GV06
GV07
GV08
GV09
GV10
GV11
GV12
GV13
GV14
GV15
GV16
GV17
GV18
GV19
GV20
GV21
GV22
GV23
GV24
GV25
GV26
GV27
GV28
CV01
CV02
CV03
CV04
CV05
CV06
CV07
CV08
CV09
CV10
CV11
CV12
CV13
CV14
CV15
CV16
CV17
CV18
CV19
CV20
CV21
CV22
CV23
CV24